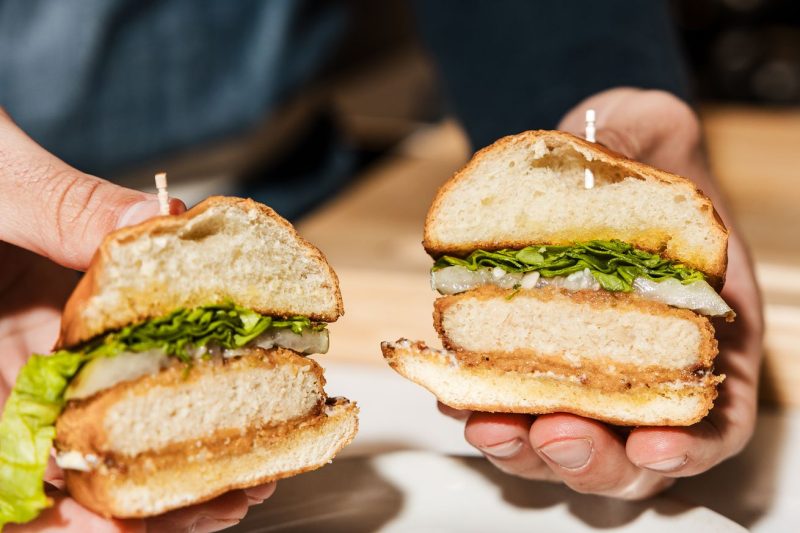
In a recent turn of events, the state of Florida finds itself in the midst of a legal battle over its ban on lab-grown meat. This ban, which prohibits the sale of meat cultivated through cell cultures rather than traditional animal rearing practices, has sparked a contentious debate between industry stakeholders, lawmakers, and advocacy groups.
The controversy surrounding lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat or cell-based meat, revolves around the potential of this emerging technology to revolutionize the food industry. Proponents argue that lab-grown meat offers a sustainable and ethical alternative to conventional animal farming, addressing key issues such as animal welfare, environmental impact, and food security. By producing meat in a controlled laboratory setting, proponents claim that lab-grown meat can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water usage associated with traditional livestock farming.
However, opponents of lab-grown meat, including traditional livestock producers and some policymakers, raise concerns about the safety, transparency, and economic impact of this nascent industry. Critics argue that lab-grown meat may not have undergone sufficient regulatory scrutiny to ensure its safety for human consumption. Moreover, there are concerns about the potential disruption to the existing meat industry, including job losses and economic implications for farmers and ranchers.
The legal challenge against Florida’s ban on lab-grown meat highlights the broader regulatory and ethical considerations surrounding food technology innovation. While some states have embraced the development of lab-grown meat as a promising solution to the challenges of conventional animal agriculture, others have taken a more cautious approach, prioritizing consumer protection and economic interests.
As the lawsuit unfolds, it will be critical to weigh the scientific, ethical, and economic implications of lab-grown meat production. Striking a balance between innovation and regulation will be essential in ensuring the successful integration of new technologies into the food system while upholding consumer trust and safety.
In conclusion, the battle over lab-grown meat in Florida serves as a microcosm of the larger debate surrounding the future of food production and sustainability. As technology continues to reshape the way we grow, process, and consume food, it is imperative that policymakers, industry stakeholders, and consumers engage in open dialogue to navigate the complex challenges and opportunities presented by innovations such as lab-grown meat. Ultimately, the resolution of this legal dispute will not only shape the trajectory of the lab-grown meat industry but also set a precedent for the regulation of emerging food technologies in the years to come.