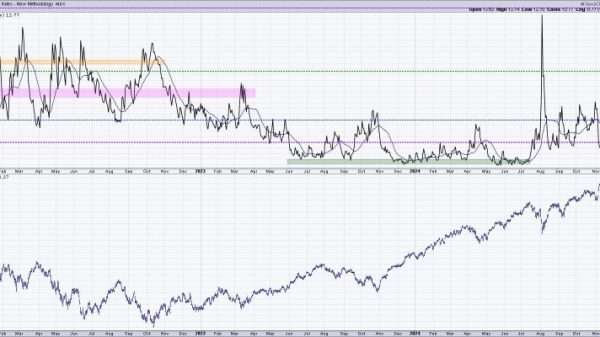
In recent years, the cobalt market has faced a significant level of volatility as the battery chemistry landscape continues to evolve. The rise of electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, and various technological advancements have led to a surge in demand for cobalt, a critical component in the production of lithium-ion batteries. However, the market is currently at a crossroads, as uncertainty looms over the future of cobalt prices due to shifting battery chemistry preferences and emerging substitutes.
One of the primary reasons for the uncertain outlook on cobalt prices is the ongoing transition towards cobalt-light or cobalt-free battery chemistries. As concerns over the environmental and ethical implications of cobalt mining have grown, battery manufacturers have been actively exploring alternative formulations that reduce or eliminate the need for cobalt. Nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM) and nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) chemistries have gained popularity in recent years due to their lower cobalt content and improved energy density. These chemistries offer comparable performance to traditional cobalt-heavy formulas, making them an attractive option for electric vehicle manufacturers and battery producers.
Additionally, the emergence of solid-state batteries has the potential to further impact the demand for cobalt. Solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes instead of liquid electrolytes, offering improved safety, energy density, and longevity compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. While solid-state batteries are still in the early stages of commercialization, their development could significantly reduce the reliance on cobalt and other scarce materials in battery manufacturing.
Moreover, advancements in recycling technologies and materials substitution efforts are expected to further dampen the demand for cobalt in the future. Recycling initiatives aimed at recovering and reusing cobalt from end-of-life batteries are gaining traction, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective solution compared to primary cobalt production. Additionally, ongoing research into alternative materials such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which use iron instead of cobalt, could potentially disrupt the cobalt market in the long term.
Despite the growing uncertainties surrounding cobalt demand, some factors continue to support the recovery of cobalt prices. The global push towards electric mobility, coupled with the increasing adoption of renewable energy systems, is expected to drive the demand for lithium-ion batteries in the coming years. Cobalt remains a crucial element in the production of high-performance batteries, especially for applications that require high energy density and power output.
In conclusion, the cobalt market is currently navigating through a period of transition as battery chemistry preferences evolve and sustainable alternatives gain momentum. While the uncertainty surrounding cobalt prices persists, the long-term outlook for the cobalt market remains positive, driven by the increasing demand for energy storage solutions and electric vehicles. Stakeholders in the cobalt industry must adapt to these changes by embracing innovation, sustainable practices, and diversification to ensure a resilient and competitive market presence in the future.